Prepare and Analyze a Plant Extract by GC
From LEAP
Current revision (13:23, 8 June 2010) (view source) |
|||
| (75 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{LSApp | {{LSApp | ||
|name = Plant Extract | |name = Plant Extract | ||
| - | |image = | + | |image = PlantExtract1.png |
|type = Sample Prep and Inject | |type = Sample Prep and Inject | ||
| - | |id = | + | |id = Plant1001 |
| - | |description = | + | |description = Analyzing a Plant Extract for Chemicals |
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{logo}} | ||
=== Overview === | === Overview === | ||
| - | + | Plant material and biomass in general are not just for food and feed any longer. They have become the feedstock for fuel, neutraceuticals, drugs and food supplements such as OMEGA-3 or other strong antioxidants. There is a growing research community that looks from a genetics and maximum yield perspective at many bio-organism. A primary example are seeds for oil or algae for OMEGA-3. All these examples have one complication in common: Before analysis for the presence of certain chemicals (molecules) an extract has to be generated out of the raw sample. Fibers, skin and other natural tissue has to be filtered and many constituants of the plants that are of interest have to be extracted in an extraction and separation process. There are many procedures that use a manual approach. As long as the methodology of plant research is its trial and error stage automation can't be justified. However, once a systematic work flow is well defined an automated process is not only more productive but leads to more consistency and less wasteful use of materials, disposables, solvents and of course highly educated personnel's time. | |
| + | [http://www.leaptec.com/ LEAP Technologies] had many customers that successfully got their extractions automated. Some started out with Seeds, Algae, Tobacco and other leafy plants. The automation was in many cases "just-in time" sample preparation on [http://www.leaptec.com/ LEAP's] primary XYZ platform the CTC PAL with a subsequent injection onto a [http://leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Category:Gas_Chromatography Gas Chromatograph] or [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Category:Mass_spectrometry Mass Spectrometer]. | ||
| - | + | Often a [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=TwinPAL GC Twin PAL] accomplishes the extraction and filtration before a GC analyzes plant extract material. The application is to take a vial containing plant material, add [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Large_Volume_Dispensing solvent], [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Agitation_of_Samples heat & agitator], [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Filtering_of_Samples filtering], and then analyze on a 7890 GC. This application may be applicable to any customer who wants to do filtration providing the liquid can be pushed thru the filter plate with a low pressure inert gas through the headspace syringe. | |
| - | == | + | Additional accessories such as an integrated [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Balance_PAL balance] and a [http://leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Bar_Code_Reading barcode scanner] have been added in the past. |
| - | + | ||
| - | * | + | '''Markets Served:'''<br> |
| + | Elements of this application can be applied to labs requiring any type of filtration of a sample while maximizing throughput. | ||
| + | * University | ||
| + | * Research | ||
| + | * FDA | ||
| + | * EPA | ||
| + | * USDA | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | '''What is a | + | '''What is a Plant Extract experiment?'''<br/> |
| - | The sample | + | The sample prep procedure is quite simple with the exception of the final sample needing to not contain any of the plant material when it gets to the analysis procedure. The samples are incubated in a [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Agitation_of_Samples heated agitator], and then allowed to settle. The sample solvent, possible containing small pieces of plant material, is filtered. LEAP has a variety of ways to filter whether it is thru a 96 well filter plate or with Uni-Prep Vials. See [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Filtering_of_Samples filtering of samples] for the different approaches. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
'''LEAPS Approach'''<br/> | '''LEAPS Approach'''<br/> | ||
| - | + | The GC [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=TwinPAL Twin PAL] in combination with the [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Category:Chronos Chronos Mastersoftware] makes a very effective and flexible workstation. We were able to design and provide a solution which met the following challenges from the customer:<br/> | |
| - | + | # Provide the necessary filtration to have clean samples to analyze. In order to get good blow-out of the liquid through the filter, it was determined that the filter plate should be sealed and have a small nozzle on the underside to ensure accurate collection without crossover to adjacent collection vials.<br/> | |
| - | + | # Throughput. By using a Twin PAL we are able to take advantage of having one PAL do the preparation while the other does the sample injections.<br/> | |
| - | + | # Spatial concerns. Provide a way to get everything that was required to fit. <br/> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<br/> | <br/> | ||
| - | + | === Photos === | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | = Photos = | + | |
| - | + | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
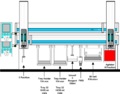
| - | Image: | + | Image:PlantExtract1.png| Automation of Plant Extract before Gas Chromatography |
| + | Image:Seed Crushing.png| Seed Crusher for hand use | ||
| + | Image:Seed_Filtration.png| LEAP Twin PAL with Agitator, 96 well plate filtration, large volume solvent, | ||
| + | Image:Filtration.png| Filtration with 96 well plate | ||
| + | Image:XPress_on_PAL.png | LEAP X-Press option on LEAP CTC PAL | ||
| + | Image:UniPrep_Filter_diagram.png | UniPrep Filter Diagram | ||
| + | Image:DISP_TOOL_Dilutor.png | Dilutor with DISPTool | ||
| + | Image:Dilutor.png | Dilutor on PAL | ||
| + | Image:Chronos_Sample_Sequence.png | Chronos software schedule | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | * Additional info on '''[http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Balance_PAL Integrated Balance]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Additional info on '''[http://leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Bar_Code_Reading Barcode Reading]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Additional info on '''[http://leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Filtering_of_Samples Filtering]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Additional info on '''[http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Shaking%2C_Heating_of_Samples Mixing of samples]''' | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Application Publications & Posters === | ||
| + | [[image: Info icon.png|40px]] [[Media:The_Plant_Journal_(2006)_45,_847-856.pdf|The Plant Journal (2006) - A high-throughput screen for genes from castor that boost | ||
| + | hydroxy fatty acid accumulation in seed oils of transgenic Arabidopsis]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Videos of PAL === | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Movie Icon.png|40px]] | ||
| + | [http://www.youtube.com/user/LEAPTechnologies#g/u LEAP's PAL Application Videos on YouTube] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | {{logo}} | ||
| + | LEAP provides automated workstation instrumentation solutions based on the LEAP CTC PAL X, Y, Z syringe only autosampler robot from LEAP Technologies. This extremely flexible, precise, and adaptable liquid handling robotic platform is available in a variety of lengths and options depending on the requirements of your sample preparation and injections for your UHPLC, LC or GC chromatography.LEAP offers full support and service for the PAL platform in addition to being able to write custom macros, cycles, and scheduling to your applications. Please contact LEAP Technologies on how we can help you get maximized throughput with flexible pipetting automation solutions. | ||
| - | + | === Contact LEAP === | |
| + | {{contact|topic=the PAL and the application}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Chronos]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Application_Solutions]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Application Publications & Posters]] | ||
Current revision

| Plant Extract |
| Application Type | |
| Sample Prep and Inject | |
| Application ID | |
| Plant1001 | |
| Description | |
| Analyzing a Plant Extract for Chemicals |
Contents |
Overview
Plant material and biomass in general are not just for food and feed any longer. They have become the feedstock for fuel, neutraceuticals, drugs and food supplements such as OMEGA-3 or other strong antioxidants. There is a growing research community that looks from a genetics and maximum yield perspective at many bio-organism. A primary example are seeds for oil or algae for OMEGA-3. All these examples have one complication in common: Before analysis for the presence of certain chemicals (molecules) an extract has to be generated out of the raw sample. Fibers, skin and other natural tissue has to be filtered and many constituants of the plants that are of interest have to be extracted in an extraction and separation process. There are many procedures that use a manual approach. As long as the methodology of plant research is its trial and error stage automation can't be justified. However, once a systematic work flow is well defined an automated process is not only more productive but leads to more consistency and less wasteful use of materials, disposables, solvents and of course highly educated personnel's time. LEAP Technologies had many customers that successfully got their extractions automated. Some started out with Seeds, Algae, Tobacco and other leafy plants. The automation was in many cases "just-in time" sample preparation on LEAP's primary XYZ platform the CTC PAL with a subsequent injection onto a Gas Chromatograph or Mass Spectrometer.
Often a GC Twin PAL accomplishes the extraction and filtration before a GC analyzes plant extract material. The application is to take a vial containing plant material, add solvent, heat & agitator, filtering, and then analyze on a 7890 GC. This application may be applicable to any customer who wants to do filtration providing the liquid can be pushed thru the filter plate with a low pressure inert gas through the headspace syringe.
Additional accessories such as an integrated balance and a barcode scanner have been added in the past.
Markets Served:
Elements of this application can be applied to labs requiring any type of filtration of a sample while maximizing throughput.
- University
- Research
- FDA
- EPA
- USDA
What is a Plant Extract experiment?
The sample prep procedure is quite simple with the exception of the final sample needing to not contain any of the plant material when it gets to the analysis procedure. The samples are incubated in a heated agitator, and then allowed to settle. The sample solvent, possible containing small pieces of plant material, is filtered. LEAP has a variety of ways to filter whether it is thru a 96 well filter plate or with Uni-Prep Vials. See filtering of samples for the different approaches.
LEAPS Approach
The GC Twin PAL in combination with the Chronos Mastersoftware makes a very effective and flexible workstation. We were able to design and provide a solution which met the following challenges from the customer:
- Provide the necessary filtration to have clean samples to analyze. In order to get good blow-out of the liquid through the filter, it was determined that the filter plate should be sealed and have a small nozzle on the underside to ensure accurate collection without crossover to adjacent collection vials.
- Throughput. By using a Twin PAL we are able to take advantage of having one PAL do the preparation while the other does the sample injections.
- Spatial concerns. Provide a way to get everything that was required to fit.
Photos
- Additional info on Integrated Balance
- Additional info on Barcode Reading
- Additional info on Filtering
- Additional info on Mixing of samples
Application Publications & Posters
![]() The Plant Journal (2006) - A high-throughput screen for genes from castor that boost
hydroxy fatty acid accumulation in seed oils of transgenic Arabidopsis
The Plant Journal (2006) - A high-throughput screen for genes from castor that boost
hydroxy fatty acid accumulation in seed oils of transgenic Arabidopsis
Videos of PAL
![]() LEAP's PAL Application Videos on YouTube
LEAP's PAL Application Videos on YouTube
LEAP provides automated workstation instrumentation solutions based on the LEAP CTC PAL X, Y, Z syringe only autosampler robot from LEAP Technologies. This extremely flexible, precise, and adaptable liquid handling robotic platform is available in a variety of lengths and options depending on the requirements of your sample preparation and injections for your UHPLC, LC or GC chromatography.LEAP offers full support and service for the PAL platform in addition to being able to write custom macros, cycles, and scheduling to your applications. Please contact LEAP Technologies on how we can help you get maximized throughput with flexible pipetting automation solutions.
Contact LEAP
For additional information about the PAL and the application, please contact LEAP Technologies. |