Category:Headspace
From LEAP
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
[[Image:HS.png|frame|Headspace]] | [[Image:HS.png|frame|Headspace]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Basic Principles of Headspace Analysis | ||
| + | |||
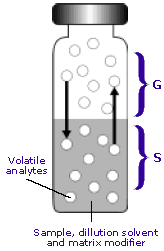
A headspace sample is normally prepared in a vial containing the sample, the dilution solvent, a matrix modifier and the headspace. Volatile components from complex sample mixtures can be extracted from non-volatile sample components and isolated in the headspace or gas portion of a sample vial. A sample of the gas in the headspace is injected into a GC system for separation of all of the volatile components. | A headspace sample is normally prepared in a vial containing the sample, the dilution solvent, a matrix modifier and the headspace. Volatile components from complex sample mixtures can be extracted from non-volatile sample components and isolated in the headspace or gas portion of a sample vial. A sample of the gas in the headspace is injected into a GC system for separation of all of the volatile components. | ||
| - | <br> | + | <br><br> |
Phases of the Headspace Vial | Phases of the Headspace Vial | ||
| - | <br> | + | <br><br> |
G = the gas phase (headspace) | G = the gas phase (headspace) | ||
The gas phase is commonly referred to as the headspace and lies above the condensed sample phase. | The gas phase is commonly referred to as the headspace and lies above the condensed sample phase. | ||
Revision as of 19:11, 28 April 2009
Basic Principles of Headspace Analysis
A headspace sample is normally prepared in a vial containing the sample, the dilution solvent, a matrix modifier and the headspace. Volatile components from complex sample mixtures can be extracted from non-volatile sample components and isolated in the headspace or gas portion of a sample vial. A sample of the gas in the headspace is injected into a GC system for separation of all of the volatile components.
Phases of the Headspace Vial
G = the gas phase (headspace)
The gas phase is commonly referred to as the headspace and lies above the condensed sample phase.
S = the sample phase The sample phase contains the compound(s) of interest. It is usually in the form of a liquid or solid in combination with a dilution solvent or a matrix modifier.
Once the sample phase is introduced into the vial and the vial is sealed, volatile components diffuse into the gas phase until the headspace has reached a state of equilibrium as depicted by the arrows. The sample is then taken from the headspace.
Pages in category "Headspace"
The following 5 pages are in this category, out of 5 total.