Sandbox
From LEAP
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
'''General Description of the Application'''<br> | '''General Description of the Application'''<br> | ||
| - | It is possible with the configuration of the PAL to automate accelerated degradation experiments | + | It is possible with the configuration of the PAL to automate accelerated degradation experiments. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
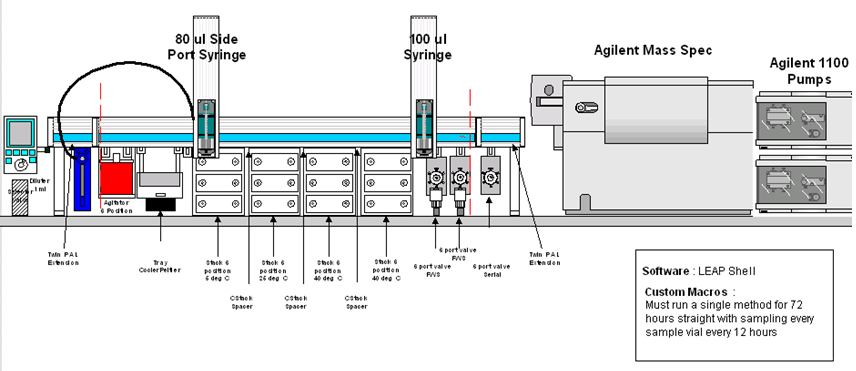
[[Image:Forced_Degredation_PAL.png|center]] | [[Image:Forced_Degredation_PAL.png|center]] | ||
| - | '''Project Ref: LS- | + | '''Project Ref: LS-FD''' |
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | '' | + | |
| - | * | + | ''Here is what our customer for this project said about Forced Degradation and the PAL at EAS 2009.''<br><br> |
| - | * | + | ''Why Automated Forced Degradation?''<br><br> |
| - | * | + | '''Why perform forced degradation studies?''' |
| + | * Evaluate API bulk and solution stability at acid, base, oxidation, thermal conditions | ||
| + | * Identify degradation route | ||
| + | * Provide guidance for bulk and formulated sample storage conditions | ||
| + | '''Current Issues: all forced degradation done manually, conditions and time are different, generate different degradates | ||
| + | '''When to perform forced degradation studies?''' | ||
| + | * Lead optimization | ||
| + | * HPLC API development/validation | ||
| + | * IND/NDA filing | ||
| + | '''Why automated forced degradation studies?''' | ||
| + | * Standardized workflow | ||
| + | * Consistent/automatic data sharing | ||
| + | * Increase productivity and efficiency | ||
| + | '''Why kinetic forced degradation studies''' | ||
| + | * Differentiate primary and second degradates | ||
| + | * Estimate degradation rate constants | ||
| + | * Define if the degradation pathway follows 1st order/ 2nd order reactions | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Bench-top Automation Platform Robotics Development Strategy''' | ||
| + | * User friendly and walk-up open access system | ||
| + | * Robust, standardized, easy to operate, straightforward to maintain | ||
| + | * Serves multiple purposes | ||
| + | * Design to work with existing data systems when required | ||
| + | * Cost effective solution that minimizes impact of multiple deployments | ||
| + | * Cycle time reduction needs outweigh high throughput centralized HTS service | ||
| + | * Lower volume and sporadic activities that require rapid response | ||
| + | * Increase productivity of time-sensitive work | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Rationale for Selection Automated System''' | ||
| + | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
=== Publications === | === Publications === | ||
Revision as of 16:30, 10 December 2009
Forced degradation is the process of subjecting drug compounds to extreme chemical and environmental conditions to determine product breakdown levels and preliminary degradation kinetics, and to identify degradant species. The stress testing practices that companies use can vary significantly and can have a serious impact on the analytical methodology used throughout the industry.
Forced degradation studies are used for multiple purposes, including demonstration of the specificity of separation methods, gaining insight into degradation pathways, and discernment of degradation products in formulations that are related to drug substances versus those that are related to other ingredients of a formulation. Reliable chemical stability testing data can show how a drug product changes over time with influence of environmental factors.
However, FDA guidance for forced degradation is vague with respect to experimental conditions. In order to harmonize the procedures of forced degradation, an automated method for forced degradation was developed, utilizing the CTC LEAP PAL workstation automation system. The Automated Forced Degradation approach significantly reduces the amount of manual labor used to perform the tests and harmonizes the operational procedures of forced degradation. The Automated Forced Degradation system is user-friendly and is intended to be used as a "walk-up system" that is able to prepare forced degradation and linearity samples, perform on-line HPLC analysis as well as generate reports automatically.
General Description of the Application
It is possible with the configuration of the PAL to automate accelerated degradation experiments.
Project Ref: LS-FD
Here is what our customer for this project said about Forced Degradation and the PAL at EAS 2009.
Why Automated Forced Degradation?
Why perform forced degradation studies?
- Evaluate API bulk and solution stability at acid, base, oxidation, thermal conditions
- Identify degradation route
- Provide guidance for bulk and formulated sample storage conditions
Current Issues: all forced degradation done manually, conditions and time are different, generate different degradates When to perform forced degradation studies?
- Lead optimization
- HPLC API development/validation
- IND/NDA filing
Why automated forced degradation studies?
- Standardized workflow
- Consistent/automatic data sharing
- Increase productivity and efficiency
Why kinetic forced degradation studies
- Differentiate primary and second degradates
- Estimate degradation rate constants
- Define if the degradation pathway follows 1st order/ 2nd order reactions
Bench-top Automation Platform Robotics Development Strategy
- User friendly and walk-up open access system
- Robust, standardized, easy to operate, straightforward to maintain
- Serves multiple purposes
- Design to work with existing data systems when required
- Cost effective solution that minimizes impact of multiple deployments
- Cycle time reduction needs outweigh high throughput centralized HTS service
- Lower volume and sporadic activities that require rapid response
- Increase productivity of time-sensitive work
Rationale for Selection Automated System
Publications
![]() EAS 2008 Poster by Merck on FD system
EAS 2008 Poster by Merck on FD system
![]() EAS 2009 Presentation by Merck on FD system
EAS 2009 Presentation by Merck on FD system
LEAP strives to find total solutions for analytical lab automation by automating analytical processes for small and large molecules in extracted liquids, solids, and recently in human, animal and plant tissues. We provide the precise robotics and efficient sample prep required by modern measurement techniques such as MALDITOF mass spectroscopy. Our newest specialty customization of CTC Analytics’ PAL features small workstations that can perform complex liquid handling tasks including HPLC-Purification, SPE, filtration, weighing, heating and stirring. They can be configured as stand alone units or integrated for “just in time” sample prep for LC-MS or GC-MS analysis. LEAP provides automated workstation instrumentation solutions based on the LEAP CTC PAL X, Y, Z syringe only autosampler robot from LEAP Technologies. This extremely flexible, precise, and adaptable liquid handling robotic platform is available in a variety of lengths and options depending on the requirements of your sample preparation and injections for your UHPLC, LC or GC chromatography.LEAP offers full support and service for the PAL platform in addition to being able to write custom macros, cycles, and scheduling to your applications. Please contact LEAP Technologies on how we can help you get maximized throughput with flexible pipetting automation solutions.
Contact LEAP
For additional information about LEAP and the PAL Platform, please contact LEAP Technologies. |