Micro Extraction by Packed Sorbent
From LEAP
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|description = Micro Extraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS) | |description = Micro Extraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS) | ||
}} | }} | ||
| - | [[Image:LEAP Logo.png|frame|www.leaptec.com<br>www.leapwiki.com]] | + | [[Image:LEAP Logo.png|frame|[http://www.leaptec.com leaptec.com]<br />[http://www.leapwiki.com leapwiki.com]]] |
| + | |||
=== Overview === | === Overview === | ||
| Line 89: | Line 90: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| - | [[Image:LEAP Logo.png|frame|www.leaptec.com<br>www.leapwiki.com]] | + | [[Image:LEAP Logo.png|frame|[http://www.leaptec.com leaptec.com]<br />[http://www.leapwiki.com leapwiki.com]]] |
| + | |||
=== Contact LEAP === | === Contact LEAP === | ||
Revision as of 18:38, 2 June 2009

| SPE Applications |
| Application Type | |
| STANDARD AND SPECIAL | |
| Application ID | |
| MEPS | |
| Description | |
| Micro Extraction by Packed Sorbent (MEPS) |
Contents |
Overview
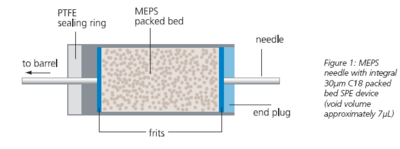
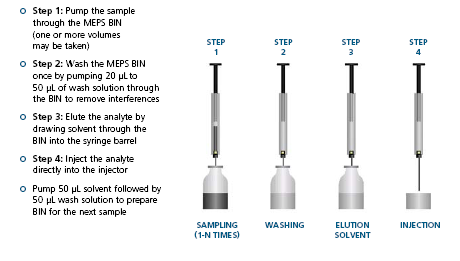
Micro Extraction by Packed Sorbent* (MEPS) is a new development in the field of sample preparation by solid phase extraction (SPE), and is a result of a collaboration between SGE and Mohamed Abdel-Rehim (AstraZeneca) and Lars G. Blomberg (University of Karlstead) Automation of MEPS is accomplished with the PAL Series of CTC Autosamplers. MEPS is the miniaturization of conventional SPE packed bed devices from milliliter bed volumes to microliter volumes. The MEPS approach to sample preparation is suitable for reversed phases, normal phases, mixed mode or ion exchange chemistries. MEPS is available in a variety of common SPE phases. The cartridge (Patent Pending) contains the stationary phase, and is built into the syringe needle. With a typical void volume of a few μL, the MEPS elution is compatible with GC and LC inlets making it ideal for automated on-line SPE on the CTC PAL platform. MEPS kits are exclusively available worldwide through LEAP Technologies and SGE Analytical Science.
MEPS performs the same function as SPE, namely the purification or speciation of samples, but with some significant differences:
- MEPS works with much smaller samples (as small as 10µL) than full scale SPE
- MEPS can be fully automated – the sample processing, extraction and injection steps are performed on-line using the same syringe
- MEPS is applicable to GC and LC
- Significantly reduces the volume of solvents and sample needed
MEPS online is an SPE solution for rapid development, in a variety of matrices; plasma, serum, whole blood, urine, aqueous
MEPS for PAL Systems is distributed by SGE & LEAP Technologies.
Benefits of MEPS
- MEPS allows SPE methodology to be applied to small sample volumes.
- MEPS can be integrated into autosampler robotics and allows on-line use of SPE.
- MEPS can reduce sample and reagent consumption and waste disposal.
- Double pass flows can reduce the weakly bound fraction.
- MEPS is field portable for remote sampling with or without the use of automated equipment.
- MEPS is adaptable for other analytical techniques including immunoassay and off-line analysis by NMR, IR and other methods.
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) has revolutionized sample preparation. Variations on the technique offer enhanced recovery, greater speciation and reduced solvent and sample consumption over other techniques.
Micro-Extraction Packed Sorbent (MEPS) is the miniaturization of conventional SPE from milliliter to microliter bed volumes that allows SPE to be used with very small samples. The manipulation of the small volumes is achieved with a precision gas tight syringe. With a typical void volume of 7μL, the MEPS
elution is compatible with GC and LC inlets making it ideal for integration into an automated sampling system for on-line SPE. In most cases, MEPS allows the same level of sample concentration as is
possible with off-line conventional SPE while providing opportunities for truly hybrid multi-dimensional methods. MEPS methods may be readily adapted from established SPE methods including those based on mixed mode or complex chemistries.
Like SPE, MEPS is for use with liquid samples (either normal or reversed phase) and yields four fractions: the unretained, weakly bound, strongly bound and irreversibly bound. However, because MEPS is a double pass system (sample and solvent enter and exit from the bottom of the bed, the weakly bound fraction (commonly the interferences eliminated by washing) is less strongly bound. The irreversibly bound fraction affects MEPS and conventional SPE and is usually associated with sorbent wetting rather than sample purification
and so the irreversible binding of matrix material from one sample does not preclude reuse of the device for a sample of the same type.
Like conventional SPE, the number of times the device can be reused is
dependent on the sample matrix. For simple applications, MEPS devices have
been used successfully for >50 cycles.
Available for both GC & LC applications. There are over 65 pre-set methods.
Significant Markets
- Natural Products
- Environmental
- Food & Beverage
- Pharmaceuticals
Sample Methods
- Aflatoxin B2 and M2 Metabolite
- Amphetamine
- Catecholamines
- Cyclosporin
- F-2 Mycotoxin
- Opiate Anagelesics
- Phthalate Esters
- Prostaglandins
- Persistent Organic Pollutants (PAH, PCB, and Pesticides)
- Steroid Acids
- S-triazine Herbicide (Atrazine)
- Vitamin A, D, and E
Photos
More Info
MEPS web site by SGE including product brochure
The Column article "It's a Small World"
The Column article "On-Site Sample Preparation Using MEPS for Wastewater Analysis
Contact LEAP
For additional information about this technique please contact LEAP Technologies for detailed information