EPA Method 8272
From LEAP
Current revision (13:17, 8 June 2010) (view source) |
|||
| (33 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
=== General Description === | === General Description === | ||
| - | U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) has method 8272 which is | + | U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) has method 8272 which is parent and alkyl polyclic aromatics in sediment pore water by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography/ mass spectrometry in selected ion monitoring mode. |
| + | |||
| + | ASTM D7363 - 07 Standard Test Method for Determination of Parent and Alkyl Polycyclic Aromatics in Sediment Pore Water Using Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry in Selected Ion Monitoring Mode | ||
| + | |||
| + | This USEPA method can be used to determine nanogram to milligram per liter PAH concentrations in pore water. | ||
The PAHs are determined using SPME followed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) analysis in selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode. | The PAHs are determined using SPME followed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) analysis in selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode. | ||
| - | Solid-Phase Microextraction: The SPME extraction of the water samples is performed using a commercially available polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-coated fused silica fiber while the water sample is mixed by the | + | Solid-Phase Microextraction: The SPME extraction of the water samples is performed using a commercially available polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-coated fused silica fiber while the water sample is mixed by the precision of the PAL autosampler agitator for mixing. |
The EPA narcosis model for benthic organisms in sediments contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) is based on the concentrations of dissolved PAHs in the interstitial water or pore water in sediment. Method 8272 covers the separation of pore water from PAH-impacted sediment samples, the removal of colloids, and the subsequent measurement of dissolved concentrations of the 10-parent PAHs and two alkylated daughter PAHs in the pore water samples. This method directly determines the concentrations of dissolved PAHs in environmental sediment pore water, groundwater, and other water samples using solid-phase microextraction (SPME) for static sample collection followed by desorption into a gas chromatograph (GC) equipped with a mass spectrometric (MS) detector operated in the selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode for analyte identification and quantitation. | The EPA narcosis model for benthic organisms in sediments contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) is based on the concentrations of dissolved PAHs in the interstitial water or pore water in sediment. Method 8272 covers the separation of pore water from PAH-impacted sediment samples, the removal of colloids, and the subsequent measurement of dissolved concentrations of the 10-parent PAHs and two alkylated daughter PAHs in the pore water samples. This method directly determines the concentrations of dissolved PAHs in environmental sediment pore water, groundwater, and other water samples using solid-phase microextraction (SPME) for static sample collection followed by desorption into a gas chromatograph (GC) equipped with a mass spectrometric (MS) detector operated in the selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode for analyte identification and quantitation. | ||
| - | These are the first | + | These are the first and only agency-approved methods for measuring PAHs in pore water. They have been used to characterize sediments and determine the actual bioavailability and toxicity of PAHs present. This method directly determines the concentrations of dissolved PAHs in environmental sediment pore water, groundwater, and other water samples. |
| - | + | SPME is a fairly new way to directly measure dissolved phase on flocculated pore waters. | |
| + | LEAP has developed a system that can add the internal standards to all of the samples with a liquid syringe and then the operator will change to the SPME fiber and run the automated method utilizing the Chronos Scheduling software. | ||
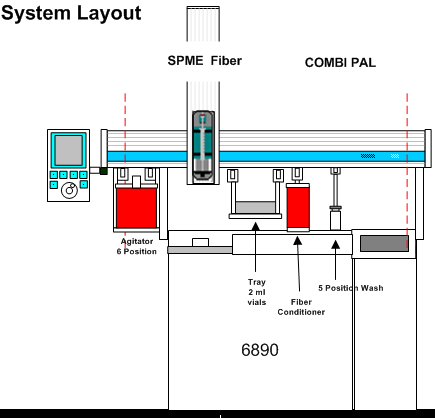
| - | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Epa_8272.png |700px|center| EPA 8272 automated system from LEAP Technologies for CTC PAL]]<br> |
<BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR> | <BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Why use LEAP to automate?=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The use of an autosampler may be used to perform the SPME extraction and the subsequent injection of collected analytes into the GC/MS. An autosampler is much preferred over the manual method because: (1) the autosampler yields lower and more reproducible blanks, (2) the manual method requires the use of a stir bar that can cause sample cross-contamination, (3) the manual method is highly labor-intensive and requires multiple timed manipulations per analysis leading to operator fatigue and resultant errors, and (4) the autosampler reduces the technician time required to prepare samples for a 24-hour run sequence to approximately 3 hours, while the manual method requires 24 hour operator attendance. | ||
| + | ---- | ||
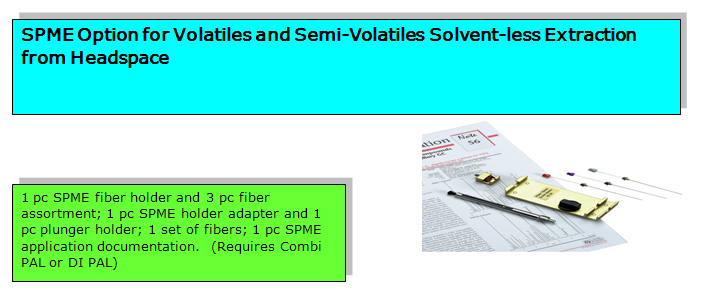
| + | [[Image:SPME Option.png |1000px|center|SPME Fiber Adapter PAL LEAP Technologies for CTC PAL]]<br> | ||
| + | <BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
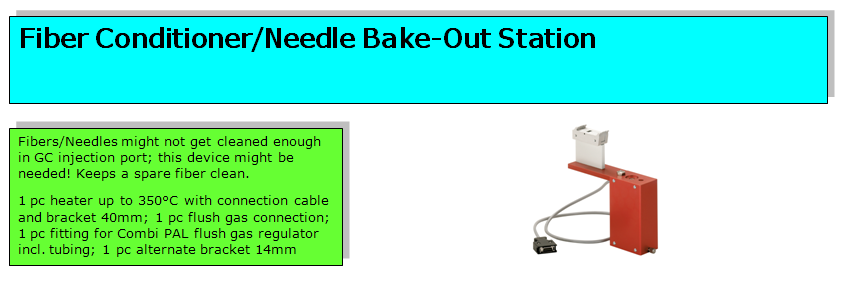
| + | [[Image:Fiber Conditioner.png|1000px|center|Fiber Conditioner PAL LEAP Technologies for CTC PAL]]<br> | ||
| + | <BR><BR><BR><BR><BR><BR> | ||
| + | ---- | ||
=== Useful links === | === Useful links === | ||
[[Image:Www icon.png|40px]] [http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/testmethods/pdfs/8272.pdf The official method at EPA .gov] | [[Image:Www icon.png|40px]] [http://www.epa.gov/epawaste/hazard/testmethods/pdfs/8272.pdf The official method at EPA .gov] | ||
| - | |||
[[Image:Www icon.png|40px]] [http://www.astm.org/Standards/D7363.htm The official ASTM Standard for D763 at ASTM.org] | [[Image:Www icon.png|40px]] [http://www.astm.org/Standards/D7363.htm The official ASTM Standard for D763 at ASTM.org] | ||
| - | [[Image:Www icon.png|40px]] [http://www. | + | [[Image:Www icon.png|40px]] [http://www.eswp.com/brownfields/Thal.pdf Advances in Bioavailability Testing, David Thal, TestAmerica Inc., Pittsburgh, PA] |
| - | + | ||
=== Video === | === Video === | ||
| Line 37: | Line 52: | ||
[[Image:Movie Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hWBjJ13h3EM Video File Movie of the COMBI with SPME in action] | [[Image:Movie Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hWBjJ13h3EM Video File Movie of the COMBI with SPME in action] | ||
| - | + | <br> | |
| - | [[Image:Movie Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.youtube.com/user/LEAPTechnologies#g/u LEAP's Videos on YouTube] | + | [[Image:Movie Icon.png|40px]] |
| + | [http://www.youtube.com/user/LEAPTechnologies#g/u LEAP's PAL Application Videos on YouTube] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
=== Accessories === | === Accessories === | ||
| - | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title= | + | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Category:Chronos Chronos Scheduling Software] |
| + | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Fiber_Conditioning Fiber Conditioning Station] | ||
[[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Agitation_of_Samples Agitation/ Mixing] | [[image:Download Icon.png|40px]] [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=Agitation_of_Samples Agitation/ Mixing] | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [ | + | Additional info on [http://www.leapwiki.com/mediawiki/index.php?title=SPME '''SPME'''] |
| + | |||
---- | ---- | ||
{{logo}} | {{logo}} | ||
LEAP provides automated workstation instrumentation solutions based on the LEAP CTC PAL X, Y, Z syringe only autosampler robot from LEAP Technologies. This extremely flexible, precise, and adaptable liquid handling robotic platform is available in a variety of lengths and options depending on the requirements of your sample preparation and injections for your UHPLC, LC or GC chromatography.LEAP offers full support and service for the PAL platform in addition to being able to write custom macros, cycles, and scheduling to your applications. Please contact LEAP Technologies on how we can help you get maximized throughput with flexible pipetting automation solutions. | LEAP provides automated workstation instrumentation solutions based on the LEAP CTC PAL X, Y, Z syringe only autosampler robot from LEAP Technologies. This extremely flexible, precise, and adaptable liquid handling robotic platform is available in a variety of lengths and options depending on the requirements of your sample preparation and injections for your UHPLC, LC or GC chromatography.LEAP offers full support and service for the PAL platform in addition to being able to write custom macros, cycles, and scheduling to your applications. Please contact LEAP Technologies on how we can help you get maximized throughput with flexible pipetting automation solutions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Keywords: 8272 PAH in by SPME and GC/MS-SIM, Method 8272 addresses the bioavailability of PAHs,ASTM D7363 - 07,USEPA 8272,Determining Bioavailable PAHs in Sediment Pore Waters,SW-846,Solid-Phase Microextraction: The SPME extraction of the water samples is performed using a commercially available polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-coated fused silica fiber while the water sample is mixed by the precession of the autosampler mixing chamber. The target PAHs and d-PAH internal standards adsorb to the nonpolar PDMS phase at equivalent rates. The use of the d-PAHs (i.e., isotopic dilution) to quantitate the target PAHs compensates for variations in equilibrium partitioning and kinetics. Liquid SPME in 2 mL vials, CombiPAL offers outstanding flexibility and productivity whether in liquid, headspace, and Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME) mode. The CombiPAL does it all. Sampling modes and sample capacity can be expanded by LEAP at any time to meet changing needs of the lab. | ||
=== Contact LEAP === | === Contact LEAP === | ||
{{contact|topic=LEAP and the PAL Platform}} | {{contact|topic=LEAP and the PAL Platform}} | ||
[[Category:Application_Solutions]] | [[Category:Application_Solutions]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Chronos]] | ||
| + | [[Category:SPME]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Example Solutions]] | ||
Current revision

| SEDIMENT PORE WATER BY SOLID-PHASE MICROEXTRACTION AND GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY/MASS SPECTROMETRY |
| Application Type | |
| SPME | |
| Application ID | |
| SPME on PAL | |
| Description | |
| EPA Method 8272 |
Contents |
General Description
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) has method 8272 which is parent and alkyl polyclic aromatics in sediment pore water by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography/ mass spectrometry in selected ion monitoring mode.
ASTM D7363 - 07 Standard Test Method for Determination of Parent and Alkyl Polycyclic Aromatics in Sediment Pore Water Using Solid-Phase Microextraction and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry in Selected Ion Monitoring Mode
This USEPA method can be used to determine nanogram to milligram per liter PAH concentrations in pore water. The PAHs are determined using SPME followed by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC/MS) analysis in selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode. Solid-Phase Microextraction: The SPME extraction of the water samples is performed using a commercially available polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-coated fused silica fiber while the water sample is mixed by the precision of the PAL autosampler agitator for mixing.
The EPA narcosis model for benthic organisms in sediments contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) is based on the concentrations of dissolved PAHs in the interstitial water or pore water in sediment. Method 8272 covers the separation of pore water from PAH-impacted sediment samples, the removal of colloids, and the subsequent measurement of dissolved concentrations of the 10-parent PAHs and two alkylated daughter PAHs in the pore water samples. This method directly determines the concentrations of dissolved PAHs in environmental sediment pore water, groundwater, and other water samples using solid-phase microextraction (SPME) for static sample collection followed by desorption into a gas chromatograph (GC) equipped with a mass spectrometric (MS) detector operated in the selected ion monitoring (SIM) mode for analyte identification and quantitation.
These are the first and only agency-approved methods for measuring PAHs in pore water. They have been used to characterize sediments and determine the actual bioavailability and toxicity of PAHs present. This method directly determines the concentrations of dissolved PAHs in environmental sediment pore water, groundwater, and other water samples.
SPME is a fairly new way to directly measure dissolved phase on flocculated pore waters.
LEAP has developed a system that can add the internal standards to all of the samples with a liquid syringe and then the operator will change to the SPME fiber and run the automated method utilizing the Chronos Scheduling software.
Why use LEAP to automate?
The use of an autosampler may be used to perform the SPME extraction and the subsequent injection of collected analytes into the GC/MS. An autosampler is much preferred over the manual method because: (1) the autosampler yields lower and more reproducible blanks, (2) the manual method requires the use of a stir bar that can cause sample cross-contamination, (3) the manual method is highly labor-intensive and requires multiple timed manipulations per analysis leading to operator fatigue and resultant errors, and (4) the autosampler reduces the technician time required to prepare samples for a 24-hour run sequence to approximately 3 hours, while the manual method requires 24 hour operator attendance.
Useful links
![]() The official method at EPA .gov
The official method at EPA .gov
![]() The official ASTM Standard for D763 at ASTM.org
The official ASTM Standard for D763 at ASTM.org
![]() Advances in Bioavailability Testing, David Thal, TestAmerica Inc., Pittsburgh, PA
Advances in Bioavailability Testing, David Thal, TestAmerica Inc., Pittsburgh, PA
Video
![]() SPME on the PAL Uses Windows Media Player to view
SPME on the PAL Uses Windows Media Player to view
![]() Video File Movie of the COMBI with SPME in action
Video File Movie of the COMBI with SPME in action
![]() LEAP's PAL Application Videos on YouTube
LEAP's PAL Application Videos on YouTube
Accessories
Additional info on SPME
LEAP provides automated workstation instrumentation solutions based on the LEAP CTC PAL X, Y, Z syringe only autosampler robot from LEAP Technologies. This extremely flexible, precise, and adaptable liquid handling robotic platform is available in a variety of lengths and options depending on the requirements of your sample preparation and injections for your UHPLC, LC or GC chromatography.LEAP offers full support and service for the PAL platform in addition to being able to write custom macros, cycles, and scheduling to your applications. Please contact LEAP Technologies on how we can help you get maximized throughput with flexible pipetting automation solutions.
Keywords: 8272 PAH in by SPME and GC/MS-SIM, Method 8272 addresses the bioavailability of PAHs,ASTM D7363 - 07,USEPA 8272,Determining Bioavailable PAHs in Sediment Pore Waters,SW-846,Solid-Phase Microextraction: The SPME extraction of the water samples is performed using a commercially available polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-coated fused silica fiber while the water sample is mixed by the precession of the autosampler mixing chamber. The target PAHs and d-PAH internal standards adsorb to the nonpolar PDMS phase at equivalent rates. The use of the d-PAHs (i.e., isotopic dilution) to quantitate the target PAHs compensates for variations in equilibrium partitioning and kinetics. Liquid SPME in 2 mL vials, CombiPAL offers outstanding flexibility and productivity whether in liquid, headspace, and Solid Phase Microextraction (SPME) mode. The CombiPAL does it all. Sampling modes and sample capacity can be expanded by LEAP at any time to meet changing needs of the lab.
Contact LEAP
For additional information about LEAP and the PAL Platform, please contact LEAP Technologies. |