Hydrogen Deuterium Exchange
From LEAP
(→Useful links) |
(→Useful links) |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
= Useful links = | = Useful links = | ||
| - | HXMS.com A good general reference site on HD Exchange theory and practice [http://www.hxms.com/hxms.htm | + | HXMS.com A good general reference site on HD Exchange theory and practice [http://www.hxms.com/hxms.htm] |
ASMS Interest Group - Hydrogen Exchange and Covalent Labeling [http://www.hxms.com/asms/] | ASMS Interest Group - Hydrogen Exchange and Covalent Labeling [http://www.hxms.com/asms/] | ||
Revision as of 21:15, 3 February 2009

| Hydrogen Deuterium Exchange |
| Application Type | |
| Sample Prep and Inject | |
| Application ID | |
| HD-X PAL | |
| Description | |
| Scheduling and Sample Prep for HD-X |
Contents |
Overview
H/D-X PAL™ is an easy-to-use, system that provides an automated process for the scheduling and experimental execution of H/D-X experimental workflow. By use of the advanced LEAP Shell scheduling software experimental design is simplified and reliable. Synchronous reagent addition and sample labeling steps are automatically scheduled to increase throughput and produce high quality data.
Protein structural studies
Information on protein structure can be obtained by one of 3 commonly used techniques:
1. Crystalography
2. NMR
3. HD Exchange
In cases where there is insufficient sample (NMR) or the protein will not crystalize, HD exchange offers an alternative option to obtain data. It is commonly used to monitor conformational changes in proteins as they relate to protein function. If conformation is altered as result of enzyme activation, drug binding or other functional events, there will likely be a change to HD exchange that can be detected.
It relies on the accurate measurement of the degree of labeling of a protein by deuterated hydrogen during a precisely measured labeling interval. The deuterium is exchanged with hydrogen atoms on the exposed amine backbone of the protein and depending on the which regions are exposed and how the protein is folded, differences are seen in the MS spectra of the digested protein when compared with non-labelled proteins.
Labelling time is important (exposure time of the protein to Deuterium) as is prevention of "back-exchange" after the labelling has occured. This is the natural tendancy of normal hydrogen to replace the deuterium after the label is removed. This is minimized by reducing the temperature of the mixture to close to zero degress Celsius.
What is an HD-X experiment ?
Performing HD-X experiments manually involves setting up many labelling mixtures then quenching these mixtures at precisely timed intervals and injecting them onto a chilled injection valve to the LCMS. In most cases a range of label times is used, from 10 seconds to several hours. Sources of error (apart from normal liquidhandling inaccuracies) are timing errors, and degradation of sample due to "back-exchange". All of these sources of error are eliminated using the automated system described here.
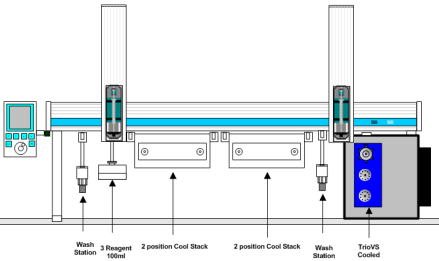
What does the H/D-X PAL do?
The instrument has two cooled zones for sample storage and labelling. The injection valve is chilled to 1 degree Celsius and includes a solvent pre-chiller and column selection valve for in-line protein digestion.
A typical experiment would consist of around a dozen time points for each protein sample, ranging from 10 seconds to 8 hours. The PAL system will schedule the experiments and perform each of the following 3 steps for each time point and sample:
Labeling The protein is mixed with a Deuterium reagent and incubated for a precisely timed interval at room temperature.
Quenching The labeling reaction is stopped by transferring a volume of the mixture to an excess of quenching reagent in a pre-cooled vessel.
Injection A measured portion of the quenched reactants is injected into a multi-column, multi-valve LCMS system. This step is synchronized with the analytical system using hardware signals. The PAL will inject samples as the LCMS system becomes ready. Labeled and quenched reactants are held in the cooled stack until they have been injected and analyzed.
Software Control
LEAP has developed a scheduling application using their proprietary software “LEAP Shell” which will automate the above labeling steps, as well as the injection to the MS and the associated chromatography.
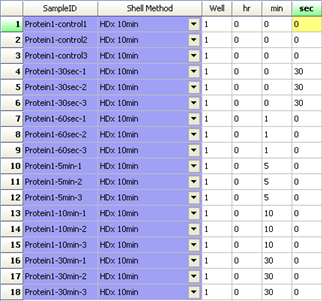
LEAP Shell Screen Shot 1: User interface to set up the labelling experiment:
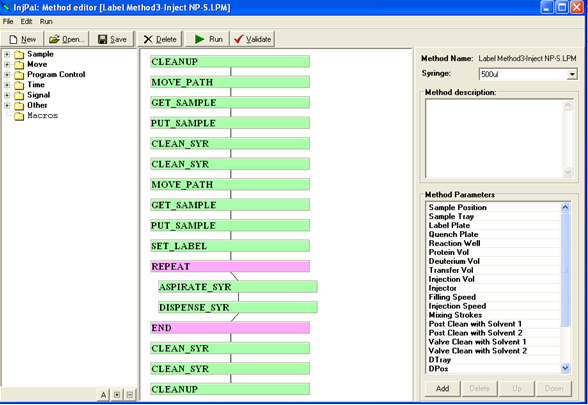
LEAP Shell Screen Shot 2: Powerfull editor for the PAL Methods:
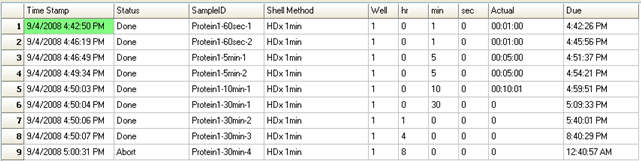
LEAP Shell Screen Shot 3: Run-time display of the labelling experiment with actual times:
Useful links
HXMS.com A good general reference site on HD Exchange theory and practice [1]
ASMS Interest Group - Hydrogen Exchange and Covalent Labeling [2]
LEAP Website H/D-x product description [3]
Publications